

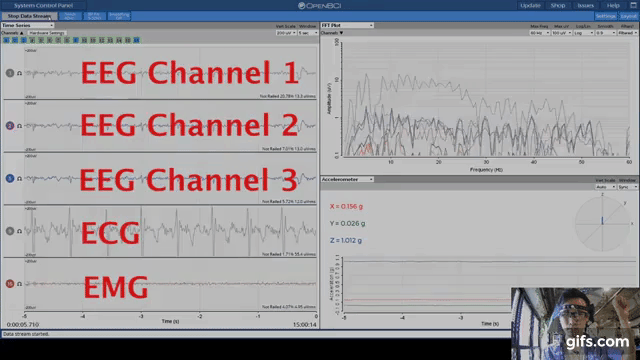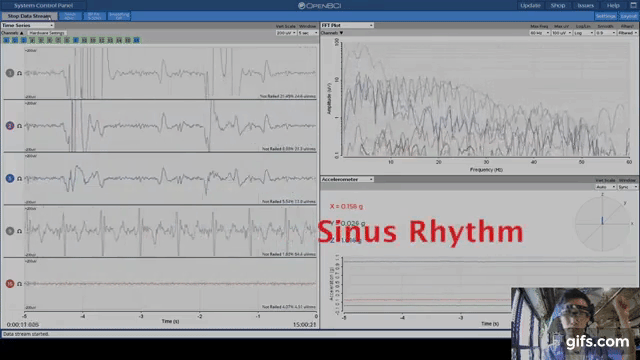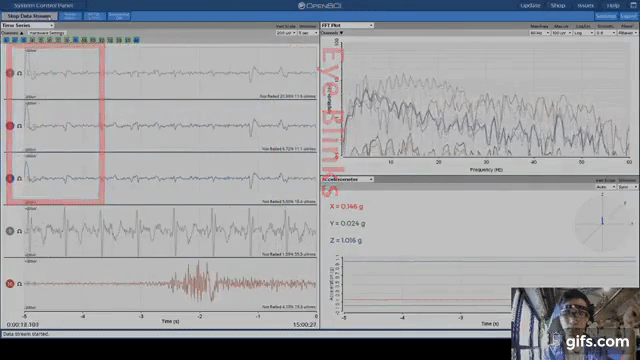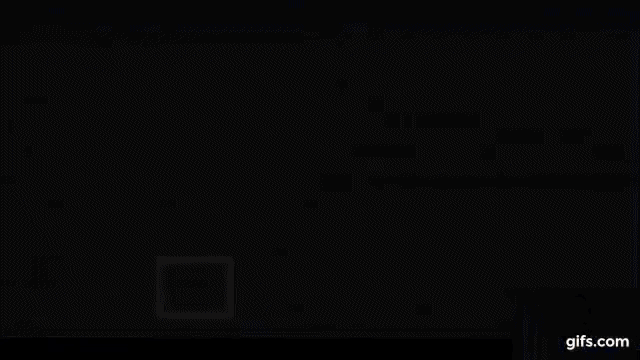
An AI was able to diagnose atrial fibrillation in normal sinus rhythm. EEG is an abbreviation of electro encephalogram, which is a method of evaluating brain’s electric activity. Typically, atrial fibrillation can only be diagnosed during an active episode.
Now, why can't reference electrodes cancel these signals out effectively on their own? I really don't have the engineering experience to know, but my guess is that the ground is just an extra measure to ensure all signals are as clear as possible. Visualized Health Visualized Study: By using clues invisible to the human eye, the AI was able to accomplish a feat not thought to be possible. You can test this out by unplugging the ground next time you do a reading you'll notice that all of the signals may become a bit "fuzzier". Most commonly it prevents 60Hz artifact caused by power sources. This could include things like electrical frequencies from power sources, currents running through the computer itself, magnetic or radio signals, etc. That means that it takes signals that all of the electrodes are reading and cancels them out of the readings.

The ground electrode is used for common mode rejection. ECGs are usually performed by attaching electrodes to the limb extremities and chest wall, which allows detection of the voltage changes generated by the myocardium during each cardiac cycle of contraction and relaxation. Electrodes fall of very easily (especially during sleep studies), and IRBs would not allow participant safety to be in the hands of something as unreliable as a small electrode that can slip off. In contrast to EEG, ECG (or EKG as it is sometimes abbreviated) is the recording of the electrical activity of the heart10. Your EEG system is not going to hurt your participants. Hey OP, please don't listen to the people here telling you the ground electrode is for safety.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
